Get to know about:
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, where data is the new currency and technology is the backbone of every operation, effective IT governance has become more crucial than ever before. IT governance encompasses the policies, processes, and structures that ensure the effective and efficient use of information technology within an organization to achieve its goals and objectives while managing risks appropriately.
As businesses increasingly rely on technology to drive innovation, enhance productivity, and gain a competitive edge, the need for robust IT governance frameworks has become paramount. Let’s delve into the importance of IT governance, its key components, best practices, and the role it plays in driving organizational success.
What is the Importance of IT Governance?
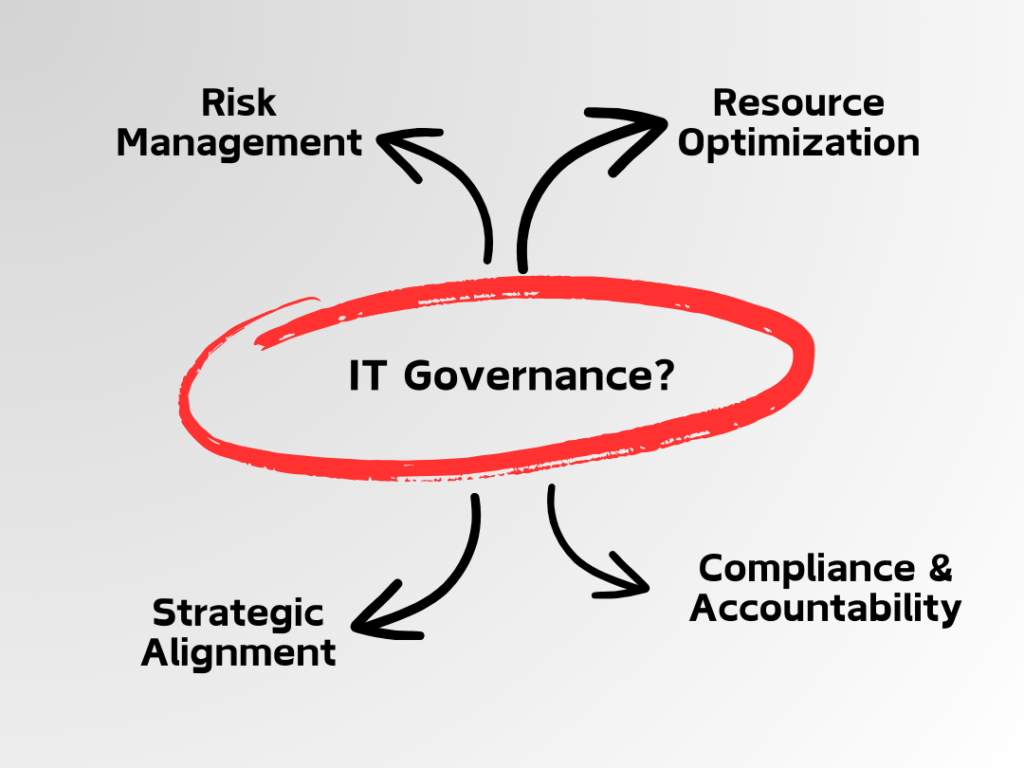
IT governance serves as the guiding force that aligns IT strategies with business objectives, ensuring that technology investments contribute to organizational growth and sustainability. Here are some key reasons why IT governance is indispensable:
Alignment with Business Goals
One of the primary reasons for the importance of IT governance is its role in aligning IT initiatives with the broader objectives of the organization. Technology is no longer just a support function but a strategic enabler of business growth and innovation. Effective IT governance ensures that investments in technology are directly linked to the organization’s strategic priorities, helping to drive revenue growth, enhance customer experiences, and gain competitive advantage.
Risk Management
In an increasingly interconnected and data-driven environment, organizations face a myriad of IT-related risks, including cybersecurity threats, data breaches, system failures, and compliance violations. IT governance provides a structured approach to identifying, assessing, and mitigating these risks, thereby protecting the organization’s assets, reputation, and stakeholder interests. By implementing robust security measures, disaster recovery plans, and compliance frameworks, organizations can minimize the impact of potential disruptions and safeguard their operations.
Resource Optimization
IT governance plays a crucial role in optimizing the allocation of resources, including budget, talent, and infrastructure. With IT budgets representing a significant portion of organizational spending, it is essential to ensure that resources are allocated efficiently and effectively. By prioritizing projects based on their alignment with strategic objectives and potential returns, IT governance helps organizations maximize the value of their investments and minimize wastage.
Compliance and Accountability
In an era of increasing regulatory scrutiny and data privacy concerns, compliance with laws, regulations, and industry standards has become non-negotiable for organizations. IT governance frameworks provide the structure and controls necessary to ensure compliance with relevant legal and regulatory requirements, such as GDPR, HIPAA, SOX, and PCI-DSS. Moreover, by establishing clear roles, responsibilities, and accountability mechanisms, IT governance promotes transparency and ethical behavior within the organization.
Components of IT Governance
IT governance encompasses various components that collectively form the framework for managing and overseeing an organization’s IT activities.
These components ensure that IT systems, processes, and investments align with the organization’s strategic objectives, manage risks effectively, optimize resource allocation, and ensure compliance with relevant regulations and standards.
Here are the 6 key components of IT governance:
1. Strategic Alignment
Strategic alignment involves ensuring that IT initiatives and investments are closely aligned with the organization’s overall business strategy and objectives.
It focuses on identifying how IT can best support the organization’s mission, vision, and goals, thereby maximizing the value of technology investments. Strategic alignment involves collaboration between IT leaders and business stakeholders to prioritize projects, allocate resources, and drive innovation in line with strategic priorities.
2. Risk Management
Risk management within IT governance involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating IT-related risks that could impact the organization’s operations, reputation, and financial stability.
This encompasses cybersecurity risks, data breaches, system failures, compliance violations, and other potential threats. Risk management strategies include implementing security controls, disaster recovery plans, and business continuity measures to minimize the impact of disruptions and protect the organization’s assets and stakeholders.
3. Resource Management
Resource management focuses on optimizing the allocation of IT resources, including budget, infrastructure, and talent, to support the organization’s objectives effectively.
This component involves identifying and prioritizing IT projects based on their strategic importance and potential returns on investment. Resource management also includes ensuring that IT assets are used efficiently, managing vendor relationships, and developing the skills and capabilities of IT personnel to meet current and future needs.
4. Performance Measurement
Performance measurement involves establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics to monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of IT governance processes and activities. It provides insights into IT performance, helps track progress towards strategic goals, and facilitates continuous improvement.
Performance measurement metrics may include uptime and availability of IT systems, response times for IT support, user satisfaction levels, and cost-effectiveness of IT investments.
5. Compliance and Legal Considerations
Compliance and legal considerations within IT governance involve ensuring that IT activities and processes comply with relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards.
It includes addressing data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and HIPAA, industry-specific regulations, such as PCI-DSS for payment card security, and internal policies and procedures. Compliance efforts may involve conducting regular audits, implementing controls and safeguards, and providing training to staff on regulatory requirements and ethical practices.
6. Decision-Making Processes
Decision-making processes within IT governance involve establishing clear mechanisms for making informed and timely decisions regarding IT investments, projects, and initiatives.
This component ensures that decision-making is transparent, accountable, and aligned with the organization’s strategic priorities. Decision-making processes may include governance structures, such as IT steering committees or project governance boards, which involve key stakeholders from IT and business units in decision-making processes.
What are best practices in IT Governance?
These best practices encompass various strategies and approaches aimed at optimizing processes and driving organizational success. Here are some key best practices in IT governance:
1. Define Clear Roles and Responsibilities
Establishing clear roles and responsibilities for IT governance stakeholders is crucial for ensuring accountability and effective decision-making. This includes defining the responsibilities of the board of directors, executive management, IT leaders, and business units in governing IT activities. By clearly defining roles and expectations, organizations can foster collaboration, reduce conflicts, and ensure that everyone understands their role in achieving IT governance objectives.
2. Establish Policies and Procedures
Developing comprehensive policies and procedures is essential for governing IT activities effectively. These policies should address various aspects of IT governance, including security protocols, risk management practices, compliance requirements, and IT project management procedures. By establishing clear guidelines and standards, organizations can ensure consistency, mitigate risks, and facilitate compliance with regulatory requirements and industry best practices.
3. Engage Stakeholders
Effective stakeholder engagement is critical for ensuring that IT governance initiatives are aligned with business objectives and stakeholder expectations. This involves fostering open communication and collaboration between IT and business stakeholders, including executives, department heads, end-users, and external partners. By involving stakeholders in decision-making processes and soliciting their input and feedback, organizations can ensure that IT governance initiatives meet the needs of the organization and its stakeholders.
4. Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
Implementing mechanisms for continuous monitoring, assessment, and improvement of IT governance practices is essential for adapting to evolving risks and opportunities. This includes establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics to measure the effectiveness of IT governance processes, conducting regular audits and assessments, and soliciting feedback from stakeholders. By continuously monitoring and evaluating IT governance practices, organizations can identify areas for improvement, address emerging risks, and enhance overall governance effectiveness.
5. Invest in Training and Education
Providing training and education programs for IT staff and business users is crucial for building awareness and understanding of IT governance principles and practices. This includes training on IT security best practices, compliance requirements, risk management techniques, and governance frameworks. By investing in training and education, organizations can empower employees to contribute to IT governance efforts, make informed decisions, and comply with policies and procedures effectively.
6. Embrace Technology Solutions
Leveraging technology solutions such as governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) platforms can streamline IT governance processes, enhance visibility, and improve decision-making. These platforms provide tools for documenting policies and procedures, managing risks and compliance requirements, automating workflow processes, and generating reports and analytics. By embracing technology solutions, organizations can increase efficiency, reduce manual efforts, and enhance the overall effectiveness of IT governance initiatives.
Conclusion
In today’s digital age, where technology permeates every aspect of business operations, robust IT governance is no longer optional—it’s imperative. By establishing clear policies, processes, and structures, organizations can effectively manage risks, optimize resources, and drive innovation to achieve their strategic objectives. Embracing best practices in IT governance enables organizations to navigate the complex digital landscape with confidence, resilience, and agility, positioning them for sustained success in an increasingly competitive environment.
Related Blogs
Create Applications with Unmatched Ease
No-Code development platform for all your unique projects.